|
Old Stuff from the Oil Fields
The Sulphur Mountain area on the northern margin of California’s Ventura basin abounds in natural tar and oil seeps. Today Sulphur Mountain is part of Santa Paula oil field.
Through the 1860’s, these tunnels produced more oil than any other method in California. Generally, crude from the tunnels was hauled by horse-drawn wagon to Ventura and shipped to San Francisco for distillation into lamp and lubricating oils.
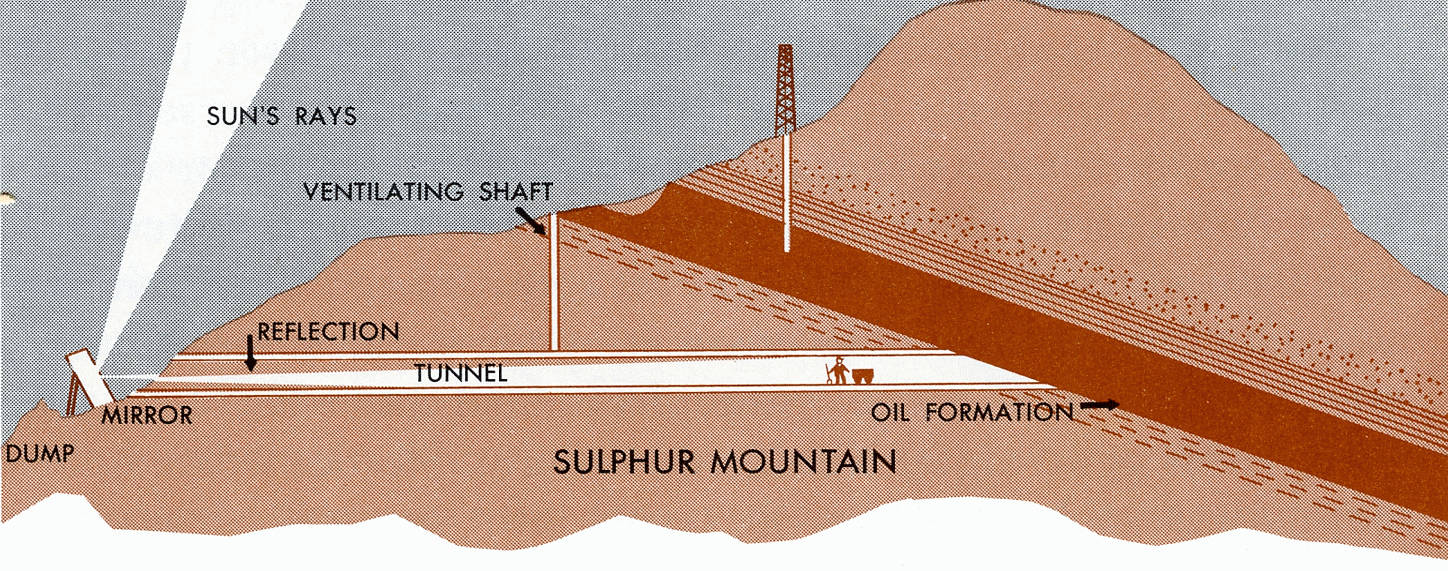
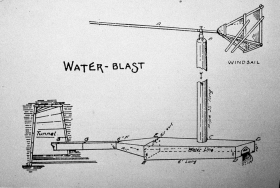
Union dug the Boarding House tunnel 1,940 feet into the base of Sulphur Mountain in the spring of 1890. As shown below, company engineers used mirrors to reflect sunlight into this tunnel for lighting and alignment, a system once used by ancient Egyptians to tunnel tombs under the mountains of Libya. Most of these tunnels were 6 feet high, 5 feet wide at the base, and 3 feet wide at the top - just large enough to accommodate a man swinging a pick. Stanford's tunnels were smaller, and simpler in construction. Oil and water collected in a shallow ditch 8 inches deep by 18 inches wide in the tunnel floors, and a one-percent grade on the floors allowed the fluids to flow downhill to the tunnel entrances. There the fluids funneled into pipes that led to collecting tanks on the outside, where the water was separated from the oil. Running boards laid on top of cross beams spread across the ditch allowed digging to continue while fluids ran down the ditch. One-ton mining cars, loaded with excavated dirt and rock, could then roll out of the tunnels on rails laid over the running boards. Water zones in the tunnels were sealed off with matched tongue-and-groove redwood lumber that gave the tunnel walls needed stability. This wood siding functioned much like the wooden casing in nearby vertical oil wells Gas vapors made tunnel digging dangerous and explosions were always imminent. Although water-laden air injected in by a water blast system could evacuate the bad air in a 560-foot tunnel in half an hour, it was difficult to adequately clear the air in longer tunnels (below).
When Union Oil had excavated the Boarding House tunnel 950 feet into Sulphur Mountain, the volatile air inside ignited with an explosion that injured four men. A second explosion a short time later killed another three. Despite these tragedies, Union finished the tunnel, extending it 1,940 feet into the mountain-deeper than most so-called “deep wells” of the day. Thirty-two of the original fifty-four tunnels were still producing in 1997, when the photos below were taken. The tunnels at this time were connected to an oil and water gathering system maintained by the Union Oil Company. This system produced about 6 to 8 barrels of oil per day, with most of the production coming from only ten of the tunnels. The locations of many of the remaining twenty-two tunnels were unknown by this time. These tunnels in 1997 produced about 750 barrels of fluid a day. However, rates increased significantly during high rainfall or when earthquakes open bedrock fractures previously sealed by asphalt. For example, tunnel production increased dramatically after the 6.8 magnitude Northridge earthquake of January 17, 1994 and was gauged three months later at 7,900 barrels of water per day with about 10 barrels of oil. This same quake also resulted in the appearance of an oil seep at nearby Ojai field where no seep had existed before. Josiah Stanford's oil tunnels were California's first horizontal oil wells. The first producing vertical well in Santa Paula field was not drilled until 1875, when it was located on a tar mat in the Adams Canyon area of Sulphur Mountain. This well, called “Old Adams”, produced 2 to 3 barrels of heavy crude each day - a meager rate even back then.
The oil produced at Sulphur Mountain comes from organic-rich shales of the Miocene Monterey Formation. After expulsion from Monterey source beds, these oils migrate to the surface through fractured bedrock of the Pliocene Sisquoc Formation that is exposed in the overturned limb of the Sulphur Mountain anticline. Although bacterial action (called biodegradation), together with evaporation and oxidation, converts the seep oils into tars and asphalts, the tunnels produce crudes that average 30.3° API.
Further Reading Clark, Michael S., Mulqueen, Steve, Chauvel, J.P. and Nichols, John, Pacific Petroleum Geologist Newsletter, Pacific Section, AAPG, September 1998, No. 7, p. 10-11. Lee, Patrick, 1989, Field In Trouble - Unocal still pumps oil the old way in Ventura County, Los Angeles Times (Newspaper), September 22, 1989. Rintoul, W., 1990, Drilling through time: California Department of Conservation, Division of Oil and Gas, Sacramento, California, 178 p. Welty, E. M. and Taylor, F. J., 1966, The 76 Bonanza: the life and times of the Union Oil Company of California: Lane Magazine and Book Company.
|
|